
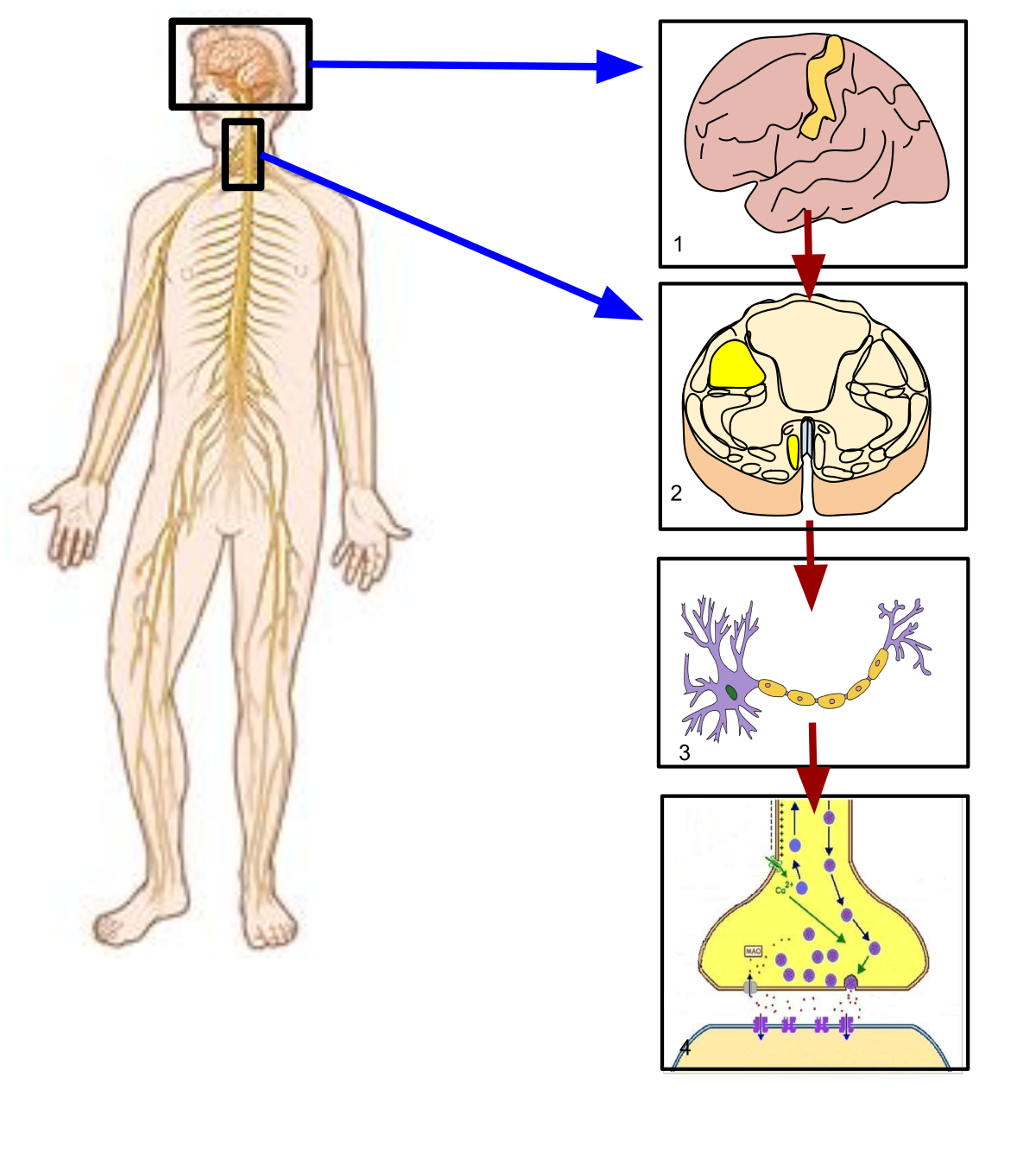
The α q-GTP complex migrates within the cell membrane and binds to and activates phospholipase C. When an agonist, such as noradrenaline, binds to the α 1-receptor, a conformational change occurs in the α q subunit of the G q protein that has two effects: GDP is released from the α q subunit and replaced by GTP, and the α q subunit (with GTP attached) detaches from the rest of the G q protein. In the inactive state, the α q subunit of the heterotrimeric G q protein is bound to GDP. The α 1-receptor is embedded in the cell membrane, where it is coupled via a G q protein to phospholipase C.
#Effector organs of the somatic nervous system are skin#
Α 1-Receptors are found in the vascular smooth muscle of the skin and splanchnic region, in the sphincters of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder, and in the radial muscle of the iris: Relatively recently, the third subsystem of neurons, known as non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic transmitters (because they use nitric oxide as a neurotransmitter), has been described and found to be integral to autonomic function, particularly in the gut and lungs.
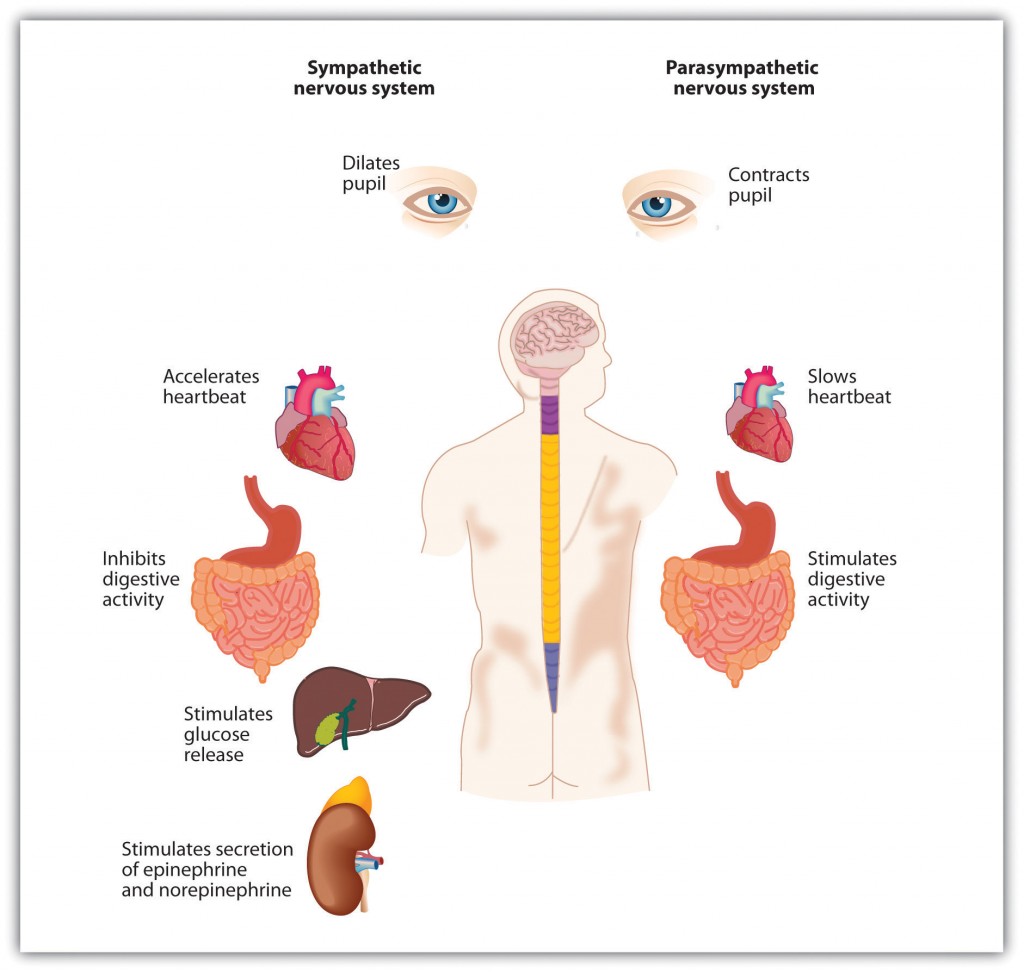
There are inhibitory and excitatory synapses between neurons. For example, stimulation of α-receptors on vessel smooth muscle induces vasoconstriction, while stimulation of β-receptors of bronchial smooth muscle induces bronchodilatation. The results of the combinations are different responses of the effector organs. It binds to two types of membrane receptors: α-adrenergic and β-adrenergic. Noradrenaline is a neurotransmitter of the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system. Nicotinic receptors are localized to the membranes of ganglionic parasympathetic and sympathetic neurons, and their activation exhibits a rapid depolarization-excitatory effect on ganglionic neurons. Their activation exhibits a slower excitatory effect. Muscarinic receptors are located on the membranes of effector cells, between the terminals of the postganglionic parasympathetic and sympathetic cholinergic fibers and effector organs. Neurotransmitters and receptors of the autonomic nervous systemĪcetylcholine binds to two types of membrane receptor: muscarinic and nicotinic. The enteric nervous system has also been referred to as the “second brain”. The main components are the plexus myentericus (Auerbach), which mainly influences motility, and the plexus submucosus (Meissner), which is responsible for glandular secretions. It is capable of acting independently of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems however, it may be modulated by sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. The enteric-or intrinsic-nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system and consists of a network of neurons that manage the functions of the gastrointestinal tract. The current view is that the sympathetic nervous system is a “quick response mobilizing system” and the parasympathetic nervous system is a “more slowly activated inhibitory system.”

In many cases, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems have “opposite” actions, in which one system activates and the other inhibits a physiological response.
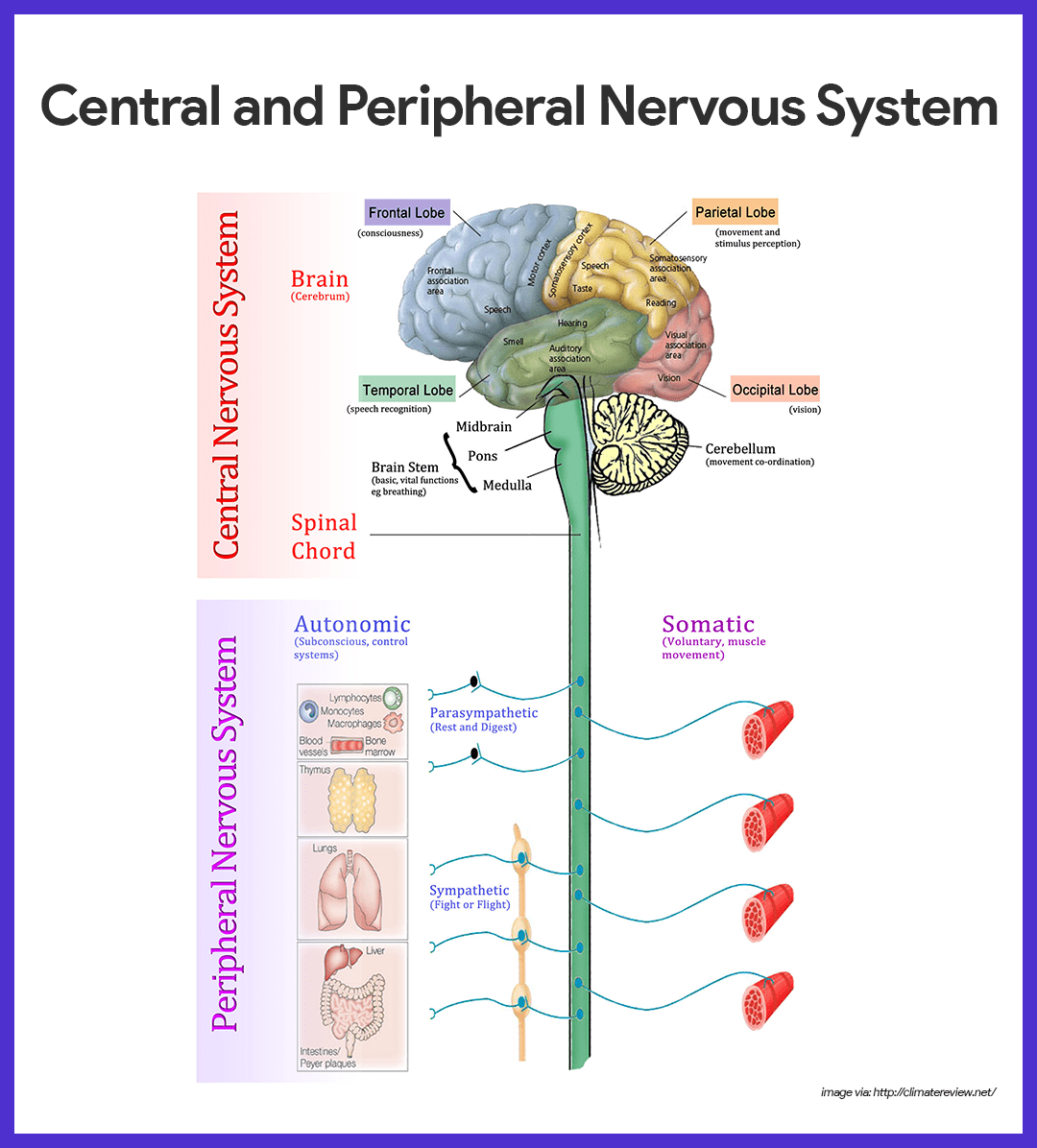
The autonomic nervous system has three branches: sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric. The autonomic nervous system innervates the smooth muscles of vessels, digestive system, bladder and urethra, lower airways, cardiac muscle, sweat and lacrimal glands, and adrenal medulla. Similarly, through the control of somatic functions, a relatively large part of autonomic regulation is controlled through the reflex arc. The autonomic (vegetative) nervous system is an involuntary system that primarily controls and modulates the functions of the visceral organs. What is the physiology of the autonomic nervous system and what do we teach students about this system in medical faculties? The sensory, somatic, and autonomic parts of the nervous system have been extensively studied. It provides neural control that is faster than hormonal pathways and is, therefore, more suitable for transmitting information that requires a rapid, coordinated response. The nervous system captures and processes stimuli acting on an organism and provides the means for an adequate response.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
